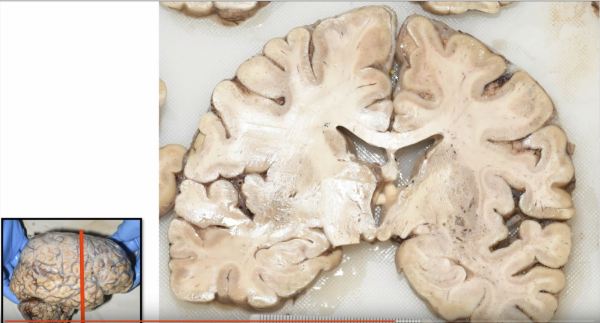
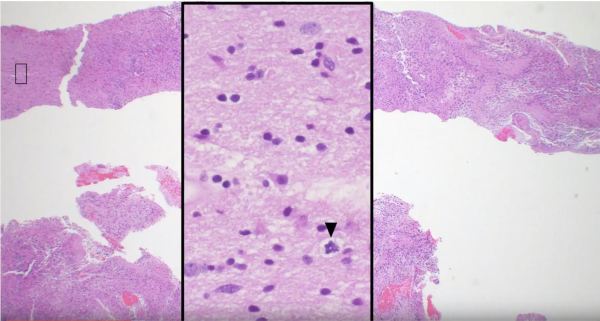
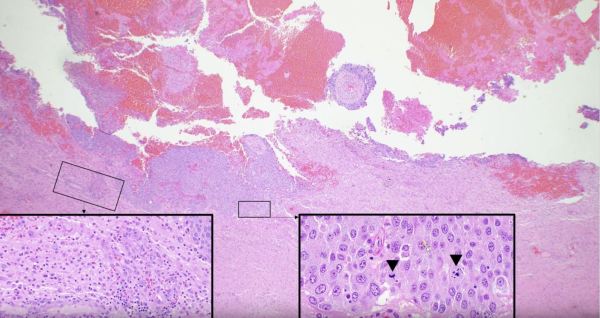
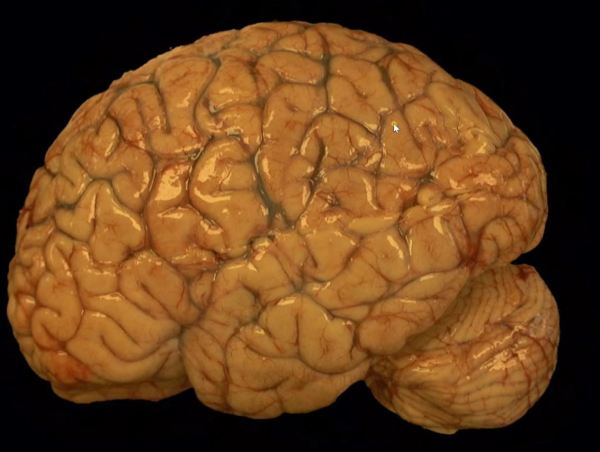
https://youtu.be/6nYyMnAxn_o Cryptococcal Meningoencephalitis explained.
Video: Bacterial ventriculitis in prematurity.
https://youtu.be/qi41D2AgzCg Learn about bacterial infections in the ventricle of a fetus.
Video: Glioblastoma Histopathologic Diagnosis
A review of the histopathologic diagnosis of the most common primary malignant brain tumor: glioblastoma. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3KD6wnMR6Lg&t=74s
Video: Carcinoma Metastasis to Brain
https://youtu.be/CHU-464bph8 Review of the histopathologic cancer diagnosis of a carcinoma metastasized to the brain.
Glioblastomas
Glioblastomas are high grade astrocytomas that often exhibit microvascular proliferation, characterized by atypical hypertrophic and hyperplastic endothelial cells. A mitotic figure within a proliferating endothelial cell is present in the top right corner of the image.
Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage
The massive intraparenchymal hemorrhage depicted in the autopsy specimen of a 60-year-old male patient is the result of hypertensive vasculopathy. Bleeding originated in penetrating vessels of the basal ganglia and extended into adjacent cerebral structures. The blood acts as a space-occupying lesion, resulting in uncal and subfalcine herniation with associated tissue destruction.
Glioblastoma with Ring Enhancement (MRI)
This middle aged patient had a heterogeneous lesion with multiple irregular rings of enhancement following contrast administration. Biopsy revealed glioblastoma with microvascular proliferation and necrosis, both of which contain leaky blood vessels that contribute to contrast enhancement on imaging.
MRI of Glioblastoma with Subfalcine Herniation
This elderly patient complaining of headache was diagnosed with glioblastoma following biopsy of the heterogeneous, ring-enhancing lesion in the right temporal lobe. Mass effect caused by the space-occupying tumor has pushed the ipsilateral cingulate gyrus under the falx cerebri, resulting in a subfalcine herniation.