Renal cell carcinoma, a relatively common cancer of the kidney, is a highly vascular lesion that will typically bleed extensively during surgery. Just prior to surgery this renal cell carcinoma that had metastasized to the paraspinal soft tissue was embolized using PVA (polyvinyl alcohol), the blue foreign embolic material within the vessel lumen. This process of embolization was... Continue Reading →
Craniopharyngioma on Gross Examination of Brain
This cystic and solid suprasellar mass, seen on this brain cut in the coronal plane, represents the classic gross appearance of a craniopharyngioma with typical focal yellow calcifications. The solid parts on gross examination correlate with enhancing regions on MRI while the cystic regions characteristically contain "machine oil"-like fluid, which is not appreciated in this... Continue Reading →
Psammoma bodies in a psammomatous variant of meningioma.
Psammoma bodies, lamellated purple concretions composed of calcium and other ions, are commonly found in meningiomas and are particularly numerous in the psammomatous variant of meningioma, pictured here. Psammomatous meningiomas are low grade (WHO grade I) tumors that often have a gritty texture on gross evaluation due to increased numbers of psammoma bodies and dystrophic calcification often necessitating... Continue Reading →
Metastatic Cancers
Metastatic cancers (i.e. cancers that originate somewhere else and travel to the brain usually via the bloodstream) can occur singly or, as pictured here, as multiple lesions. Sometimes brain metastases represent the initial clue that the person has cancer somewhere else in the body, as was the case for this patient who was found to have three enhancing cerebral lesions... Continue Reading →
Intraventricular Meningioma
Although meningiomas are classically dura-based lesions, they can also arise in the choroid plexus and, thus, must be considered in the differential diagnosis for intraventricular lesions. This intraventricular meningioma, shown here, is growing underneath normal choroid plexus epithelium.
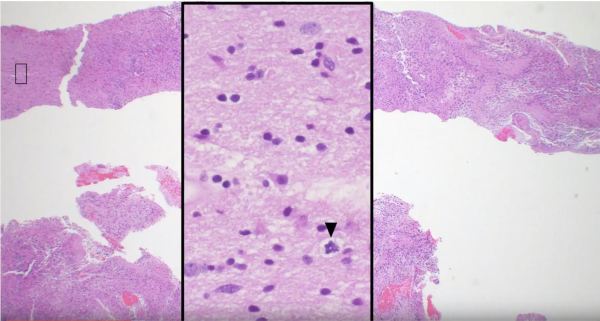
Video: Ependymomas explained.
Ependymomas are glial tumors that commonly harbor perivascular pseudo-rosettes, seen here, characterized by radially arranged tumor cells around a blood vessel core. https://youtu.be/UXDIYV_yMro
Video: Glioblastoma Histopathologic Diagnosis
A review of the histopathologic diagnosis of the most common primary malignant brain tumor: glioblastoma. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3KD6wnMR6Lg&t=74s
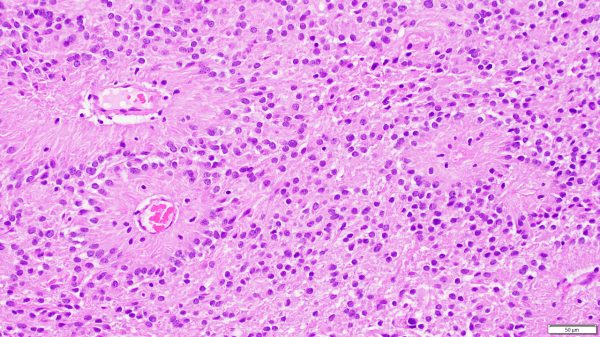
Glioblastomas
Glioblastomas are high grade astrocytomas that often exhibit microvascular proliferation, characterized by atypical hypertrophic and hyperplastic endothelial cells. A mitotic figure within a proliferating endothelial cell is present in the top right corner of the image.
Glioblastoma with Ring Enhancement (MRI)
This middle aged patient had a heterogeneous lesion with multiple irregular rings of enhancement following contrast administration. Biopsy revealed glioblastoma with microvascular proliferation and necrosis, both of which contain leaky blood vessels that contribute to contrast enhancement on imaging.
MRI of Glioblastoma with Subfalcine Herniation
This elderly patient complaining of headache was diagnosed with glioblastoma following biopsy of the heterogeneous, ring-enhancing lesion in the right temporal lobe. Mass effect caused by the space-occupying tumor has pushed the ipsilateral cingulate gyrus under the falx cerebri, resulting in a subfalcine herniation.